-40%
1997 CONGO Ferdinand von Zeppelin AVIATION Flight 1000 Francs Silver Coin i76809
$ 141.84
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
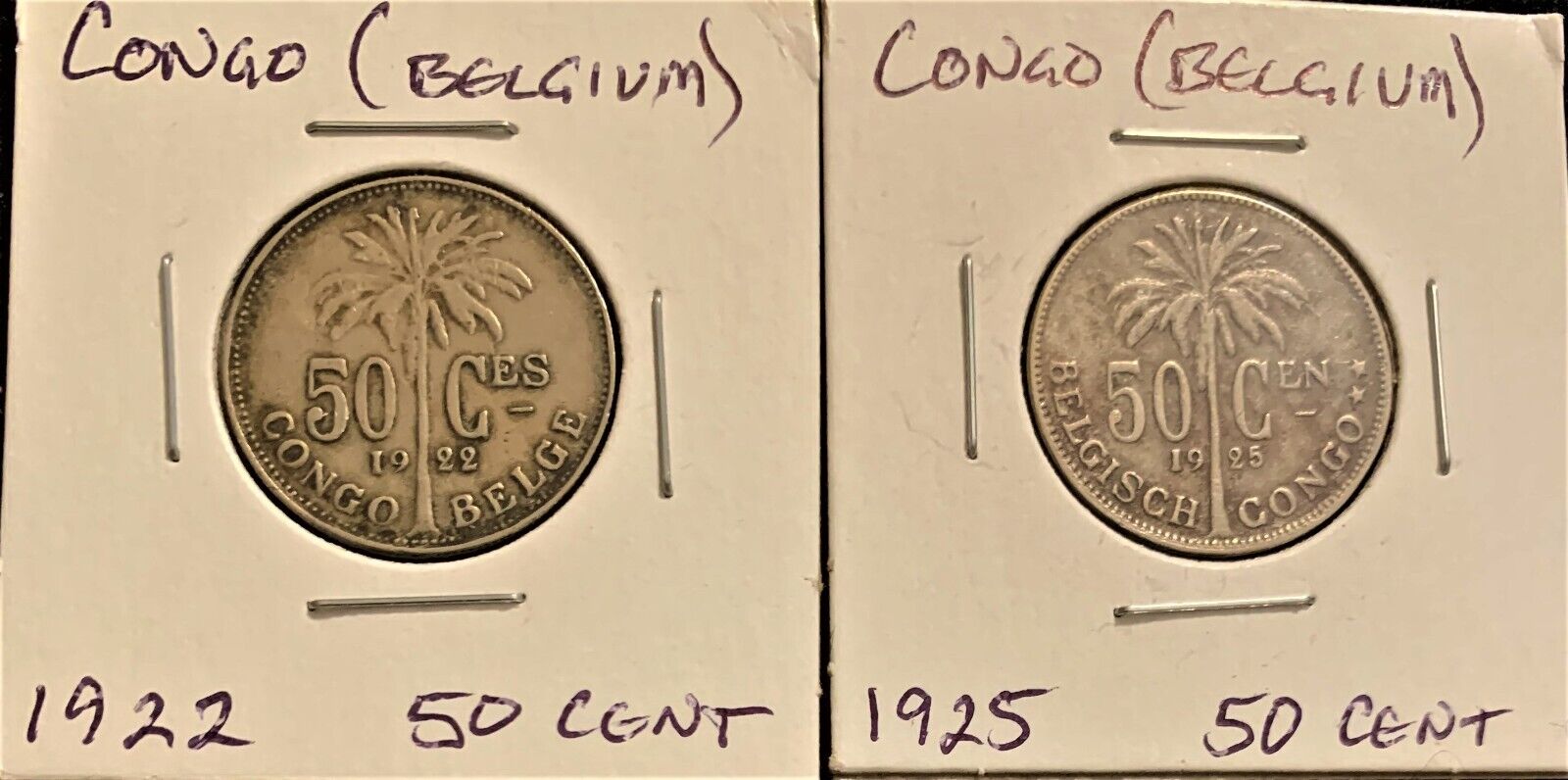
Item:i76809
Authentic Coin of:
Congo - Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin
1997
Silver 1000 Francs 35mm (
15.09
grams) 0.999 Silver (0.4818 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 37
FERDINAND GRAF VON ZEPPELIN LZ 127 1917-1997, Zeppelin motif.
REPUBLIQUE DU CONGO 1000 FRANCS, Woman seated with tablet.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Ferdinand Adolf Heinrich August Graf von Zeppelin
(8 July 1838 - 8 March 1917) was a German general and later inventor of the Zeppelin rigid airships; he founded the company Luftschiffbau Zeppelin.
Airships
Ferdinand von Zeppelin served as an official observer with the Union Army during the American Civil War. During the Peninsular Campaign, he visited the balloon camp of Thaddeus S. C. Lowe shortly after Lowe's services were terminated by the Army. Von Zeppelin then travelled to St. Paul, MN where the German-born former Army balloonist John Steiner offered tethered flights. His first ascent in a balloon, made at Saint Paul, Minnesota during this visit, is said to have been the inspiration of his later interest in aeronautics.
Zeppelin's ideas for large airships were first expressed in a diary entry dated 25 March 1874. Inspired by a recent lecture given by Heinrich von Stephan on the subject of "World Postal Services and Air Travel", he outlined the basic principle of his later craft: a large rigidly-framed outer envelope containing a number of separate gasbags. In 1887 the success of Charles Renard and Arthur Krebs' airship
La France
prompted him to send a letter to the King of Württemberg about the military necessity for dirigibles and the lack of German development in this field.
After his resignation from the army in 1891 at age 52, Zeppelin devoted his full attention to airships. He hired the engineer Theodor Gross to make tests of possible materials and to assess available engines for both fuel efficiency and power-to-weight ratio. He also had air propellers tested and strove to obtain higher purity hydrogen gas from suppliers. Zeppelin was so confident of his concept that in June 1891 he wrote to the King of Württemberg's secretary, announcing he was to start building, and shortly after requested a review from the Prussian Army's Chief of General Staff. The next day Zeppelin almost gave up as he realized he had underestimated air resistance, but resumed work on hearing that Rudolf Hans Bartsch von Sigsfeld made light but powerful engines, information soon shown to be overoptimistic. Whereupon Zeppelin urged his supporter Max von Duttenhofer to press Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft for more efficient engines so as not to fall behind the French. Duttenhofer wrote to Gross threatening to withdraw support, and Zeppelin shortly afterwards sacked Gross, citing Gross' lack of support and writing that he was "an obstacle in my path".
Despite these setbacks Zeppelin's organization had refined his idea: a rigid aluminium framework covered in a fabric envelope; separate multiple internal gas cells, each free to expand and contract thus obviating the need for ballonets; modular frame allowing addition of sections and gas cells; controls, engines and gondola rigidly attached. After publishing the idea in March 1892 he hired the engineer Theodor Kober who started work testing and further refining the design. Zeppelin submitted Kober's 1893 detailed designs to the Prussian Airship Service, whose committee reviewed it in 1894. In June 1895 this committee recommended minimum funds be granted, but withdrew this offer and rejected the design in July.
One month later, in August 1895, Zeppelin received a patent for Kober's design, described as an "airship-train" (
Lenkbarer Luftfahrzug mit mehreren hintereinanderen angeordneten Tragkörpern
[Steerable airship-train with several carrier structures arranged one behind another].) The patent describes an airship consisting of three rigid sections flexibly connected. The front section, intended to contain the crew and engines, was 117.35 m (385.0 ft) long with a gas capacity of 9514 cu m (336,000 cu ft): the middle section was 16 m (52 ft 6 in) long with an intended useful load of 599 kg (1,321 lb) and the rear section 39.93 m (131.0 ft) long with an intended load of 1,996 kg (4,400 lb)
In early 1896, Zeppelin's lecture on steerable airship designs given to the Association of German Engineers (VDI) so impressed them that the VDI launched a public appeal for financial support for him. This led to a first contact with Carl Berg who supplied aluminium alloys which Zeppelin had tested, and by May 1898 they, together with Philipp Holzmann, Daimler, Max von Eyth, Carl von Linde, and Friedrich Voith, had formed the joint stock company
Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Luftschiffart
. Zeppelin invested 441,000 Marks, over half the total capital. Actual construction then started of what was to be the first successful rigid airship, the Zeppelin LZ1.
Berg's involvement with the project would later be the cause of allegations that Zeppelin had used the patent and designs of David Schwarz's airship of 1897. Berg had signed a contract with Schwartz under the terms of which he undertook not to supply aluminium to any other airship manufacturer. He later made a payment to Schwartz's widow as compensation for dissolving this arrangement. Claims that Zeppelin had been influenced by Schwartz were denied by Eckener in 1938 and also rejected by later historians. Zeppelin's design was "radically different" in both its scale and its framework from that of Schwarz.
On 2 July 1900, Zeppelin made the first flight with the LZ 1 over Lake Constance near Friedrichshafen in southern Germany. The airship rose from the ground and remained in the air for 20 minutes, but was damaged on landing. After repairs and some modifications two further flights were made by LZ 1 in October 1900, However the airship was not considered successful enough to justify investment by the government, and since the experiments had exhausted Count Zeppelins funds, he was forced to suspend his work.
Zeppelin still enjoyed the support of the King of Württemberg, who authorised a state lottery which raised 124,000 marks. A contribution of 50,000 marks was received from Prussia, and Zeppelin raised the remainder of the necessary money by mortgaging his wife's estates. Still supported by Daimler and Carl Berg, construction of his second airship, the LZ 2, was started in April 1905. It was completed by 30 November, when it was first taken out of its hangar, but a ground-handling mishap caused the bows to be pulled into the water, damaging the forward control surfaces. Repairs were completed by 17 January 1906, when LZ 2 made its only flight. Too much ballast was jettisoned on takeoff, causing the airship to rise to an altitude of 427 m (1,401 ft). Here a stiff breeze was encountered, and although the airship was at first able to overcome this, the failure of the forward engine due to cooling problems followed by the failure of the other due to a broken clutch-spring left the airship at the mercy of the wind. It was brought down near Kisslegg in the Allgäu mountains, with some damage caused by the stern's striking some trees during mooring, but was more severely damaged by high winds the following night, and had to be dismantled.
In May 1906, work as started on a third airship, LZ 3. This was the same size and configuration as LZ 2, but had a greater gas capacity. Finished by the end of the year, it made two successful flights at a speed of 30 miles per hour (48 km/h), and in 1907 attained a speed of 36 miles per hour (58 km/h). The success of LZ 3 produced a change in the official attitude to his work, and the Reichstag voted that he should be awarded 500,000 marks to continue his work. However the purchase by the Government of an airship was made conditional on the successful completion of a 24‑hour trial flight. Knowing that this was beyond the capabilities of LZ 3, work was started on a larger airship, the LZ 4. This first flew on 20 June 1908. The final financial breakthrough only came after the Zeppelin LZ 4 was destroyed by fire at Echterdingen after breaking free of its moorings during a storm. The airship's earlier flights had excited public interest in the development of the airships, and a subsequent collection campaign raised over 6 million German marks. The money was used to create the 'Luftschiffbau-Zeppelin GmbH' and the Zeppelin foundation (
Zeppelin Stiftung
).
Following the destruction of LZ 4, LZ 3, which had been damaged when the floating hangar broke free of its mooring during a storm, was repaired: at the same time it was lengthened by 8 m. It was re-inflated on 21 October 1908 and after a series of short test flights a flight lasting 5 hours 55 minutes took place on 27 October with the Kaiser's brother, Admiral Prince Heinrich, on board. On 7 November, with Crown Prince William as a passenger, it flew 80 km (50 mi) to Donaueschingen, where the Kaiser was then staying. In spite of poor weather conditions, the flight succeeded: two days later LZ 3 was officially accepted by the Government and on 10 November Zeppelin was rewarded with an official visit to Friedrichshafen by the Kaiser, during which a short demonstration flight over Lake Constance was made and Zeppelin awarded the Order of the Black Eagle.
Although a replacement for LZ 4, the LZ 5 was built and accepted into Army service as L II, Zeppelin's relationship with the military authorities continued to be poor, and deteriorated considerably due to his criticism of the Army following the loss of L II, which was carried away from its moorings and wrecked on 25 April 1910. However, the business director of Luftschiffbau-Zeppelin, Alfred Colsman, came up with a scheme to capitalise on the public enthusiasm for Zeppelin's airships by establishing a passenger-carrying business.
Up until 1914 the German Aviation Association (
Deutsche Luftschiffahrtsgesellschaft
or DELAG) transported 37,250 people on over 1,600 flights without an incident.
[34]
Within a few years the zeppelin revolution began creating the age of air transportation.
A
Zeppelin
is a type of rigid airship named after the German Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874 and developed in detail in 1893. They were patented in Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word
zeppelin
came to be commonly used to refer to all rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins as bombers and scouts, killing over 500 people in bombing raids in Britain.
The defeat of Germany in 1918 temporarily slowed down the airship business. Although DELAG established a scheduled daily service between Berlin, Munich, and Friedrichshafen in 1919, the airships built for this service eventually had to be surrendered under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, which also prohibited Germany from building large airships. An exception was made allowing the construction of one airship for the US Navy, which saved the company from extinction. In 1926, the restrictions on airship construction were lifted, and with the aid of donations from the public, work was started on the construction of LZ 127
Graf Zeppelin
. This revived the company's fortunes, and during the 1930s, the airships
Graf Zeppelin
and the larger LZ 129
Hindenburg
operated regular transatlantic flights from Germany to North America and Brazil. The Art Deco spire of the Empire State Building was originally designed to serve as a mooring mast for Zeppelins and other airships, although it was found that high winds made this impossible and the plan was abandoned. The
Hindenburg
disaster in 1937, along with political and economic issues, hastened the demise of the Zeppelins.
The
Democratic Republic of the Congo
, also known as
DR Congo
, the
DRC
,
DROC
,
Congo-Kinshasa
, or simply
the Congo
, is a country located in Central Africa. It is sometimes anachronistically referred to by its former name of Zaire, which was its official name between 1971 and 1997. It is, by area, the largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa, the second-largest in all of Africa (after Algeria), and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of over 78 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populated officially Francophone country, the fourth-most-populated country in Africa, and the 16th-most-populated country in the world. Currently, eastern DR Congo is the scene of ongoing military conflict in Kivu, since 2015.
Centred on the Congo Basin, the territory of the DRC was first inhabited by Central African foragers around 90,000 years ago and was reached by the Bantu expansion about 3,000 years ago. In the west, the Kingdom of Kongo ruled around the mouth of the Congo River from the 14th to 19th centuries. In the centre and east, the kingdoms of Luba and Lunda ruled from the 16th and 17th centuries to the 19th century. In the 1870s, just before the onset of the Scramble for Africa, European exploration of the Congo Basin was carried out, first led by Henry Morton Stanley under the sponsorship of Leopold II of Belgium. Leopold formally acquired rights to the Congo territory at the Berlin Conference in 1885 and made the land his private property, naming it the Congo Free State. During the Free State, the colonial military unit, the
Force Publique,
forced the local population to produce rubber, and from 1885 to 1908, millions of Congolese died as a consequence of disease and exploitation. In 1908, Belgium, despite initial reluctance, formally annexed the Free State, which became the Belgian Congo.
The Belgian Congo achieved independence on 30 June 1960 under the name Republic of the Congo. Congolese nationalist Patrice Lumumba was elected the first Prime Minister, while Joseph Kasa-Vubu became the first President. Conflict arose over the administration of the territory, which became known as the Congo Crisis. The provinces of Katanga, under Moïse Tshombe, and South Kasai attempted to secede. After Lumumba turned to the Soviet Union for assistance in the crisis, the U.S. and Belgium became wary and oversaw his removal from office by Kasa-Vubu on 5 September and ultimate execution by Belgian-led Katangese troops on 17 January 1961. On 25 November 1965, Army Chief of Staff Joseph-Désiré Mobutu, who later renamed himself Mobutu Sese Seko, officially came into power through a coup d'état. In 1971, he renamed the country Zaire. The country was run as a dictatorial one-party state, with his Popular Movement of the Revolution as the sole legal party. Mobutu's government received considerable support from the United States, due to its anti-communist stance during the Cold War. By the early 1990s, Mobutu's government began to weaken. Destabilisation in the east resulting from the 1994 Rwandan genocide and disenfranchisement among the eastern Banyamulenge (Congolese Tutsi) population led to a 1996 invasion led by Tutsi FPR-ruled Rwanda, which began the First Congo War.
On 17 May 1997, Laurent-Désiré Kabila, a leader of Tutsi forces from the province of South Kivu, became President after Mobutu fled to Morocco, reverting the country's name to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Tensions between President Kabila and the Rwandan and Tutsi presence in the country led to the Second Congo War from 1998 to 2003. Ultimately, nine African countries and around twenty armed groups became involved in the war, which resulted in the deaths of 5.4 million people. The two wars devastated the country. President Laurent-Désiré Kabila was assassinated by one of his bodyguards on 16 January 2001 and was succeeded eight days later as President by his son Joseph.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is extremely rich in natural resources but has had political instability, a lack of infrastructure, issues with corruption and centuries of both commercial and colonial extraction and exploitation with little holistic development. Besides the capital Kinshasa, the two next largest cities Lubumbashi and Mbuji-Mayi are both mining communities. DR Congo's largest export is raw minerals, with China accepting over 50% of DRC's exports in 2012. In 2016, DR Congo's level of human development was ranked 176th out of 187 countries by the Human Development Index. As of 2018, around 600,000 Congolese have fled to neighbouring countries from conflicts in the centre and east of the DRC. Two million children risk starvation, and the fighting has displaced 4.5 million people. The sovereign state is a member of the United Nations, Non-Aligned Movement, African Union, and COMESA.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin
, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "
Guide on How to Use My Store
" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.